A) medial (tibial) collateral ligament (MCL)
B) posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
C) anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
D) lateral (fibular) collateral ligament (LCL)
E) lateral meniscus
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does NOT occur due to the effects of aging on the joints?
A) decreased range of motion
B) decreased flexibility and elasticity
C) increased production of synovial fluid
D) weakening of muscles
E) decreased tissue repair
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning sutures is false?
A) They may become completely immovable in adults.
B) The opposing bones in the joint interdigitate for stability.
C) The tissue between the bones is hyaline cartilage.
D) The periosteum of adjacent bones is continuous over the joint.
E) Membranes, called fontanels, are present in some sutures at birth.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The epiphyseal plate of a growing bone is actually a temporary joint called a
A) synchondrosis.
B) synostosis.
C) syndesmosis.
D) symphysis.
E) suture.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The opposite of depression is
A) inversion.
B) protraction.
C) elevation.
D) pronation.
E) flexion.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The muscles that hold the humeral head within the glenoid cavity are collectively called the
A) sunacromial bursae.
B) rotator cuff.
C) glenoid labrum.
D) coracohumeral ligament.
E) deltoid muscle.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sagittal suture is between the
A) sacrum and coxa.
B) two pubic bones.
C) atlas and axis.
D) alveolar process and tooth.
E) two parietal bones.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The joint between the head of the radius and the proximal end of the ulna is a _____ joint.
A) plane
B) saddle
C) hinge
D) pivot
E) ball and socket
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A biaxial joint has movement
A) around one axis.
B) around two axes at right angles to one another.
C) about several axes.
D) as long as there is articular cartilage present.
E) that always rotates.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
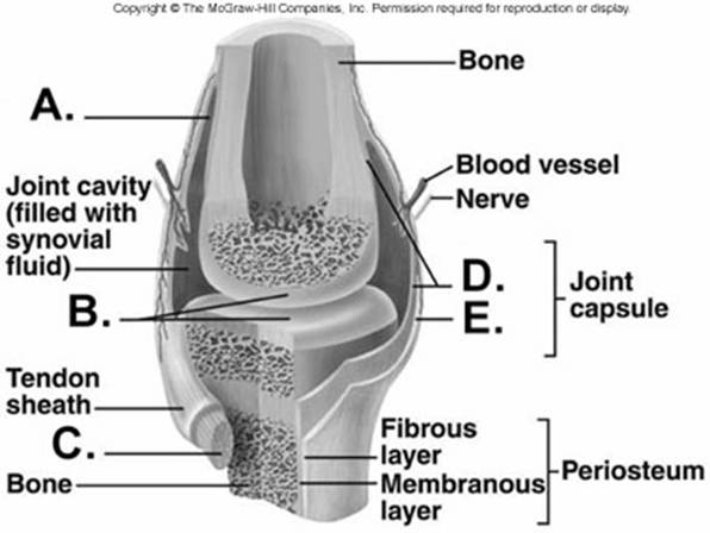 -What does structure "C" represent on the diagram?
-What does structure "C" represent on the diagram?
A) tendon
B) articular cartilage
C) bursa
D) fibrous capsule
E) synovial membrane
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Synovial joints are different from both fibrous and cartilaginous joints because synovial joints
A) use fibrous connective tissue to hold the bones in the joint together.
B) are enclosed by a joint capsule.
C) are only temporary; they are replaced in the adult.
D) generally have both bones in the joint fused together.
E) are not freely moveable.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Abnormal forced extension beyond normal range of motion is called
A) circumduction.
B) rotation.
C) hyperextension.
D) supination.
E) pronation.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sharp object penetrated a synovial joint. From the following list of structures, select the order in which they were penetrated. (1) tendon or muscle (2) ligament (3) fibrous capsule (4) skin (5) synovial membrane
A) 4, 1, 2, 5, 3
B) 4, 5, 1, 2, 3
C) 4, 3, 2, 5, 1
D) 4, 1, 2, 3, 5
E) 4, 2, 1, 5, 3
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
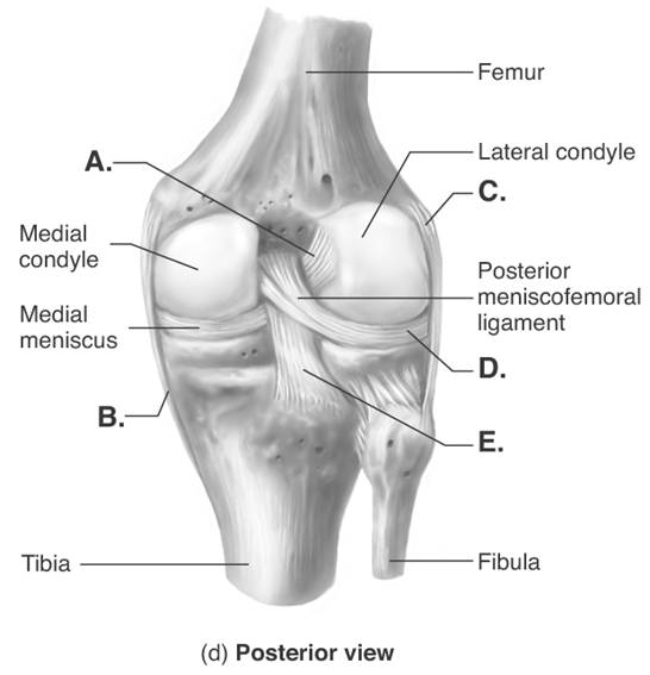 -The figure illustrates a posterior view of the right knee joint. What does "A" represent?
-The figure illustrates a posterior view of the right knee joint. What does "A" represent?
A) medial (tibial) collateral ligament (MCL)
B) posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
C) anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
D) lateral (fibular) collateral ligament (LCL)
E) lateral meniscus
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning the ankle joint is true?
A) The calcaneus articulates with the tibia to form this joint.
B) Most common injuries to this joint occur because of a forceful inversion of the foot.
C) A capsule of hyaline cartilage surrounds the joint.
D) The lateral collateral ligament helps to stabilize this joint.
E) It is a pivot joint.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The opposite of eversion is
A) inversion.
B) protraction.
C) elevation.
D) pronation.
E) flexion.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The knee joint is an example of a _____ joint.
A) plane
B) saddle
C) pivot
D) ball and socket
E) complex ellipsoid
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
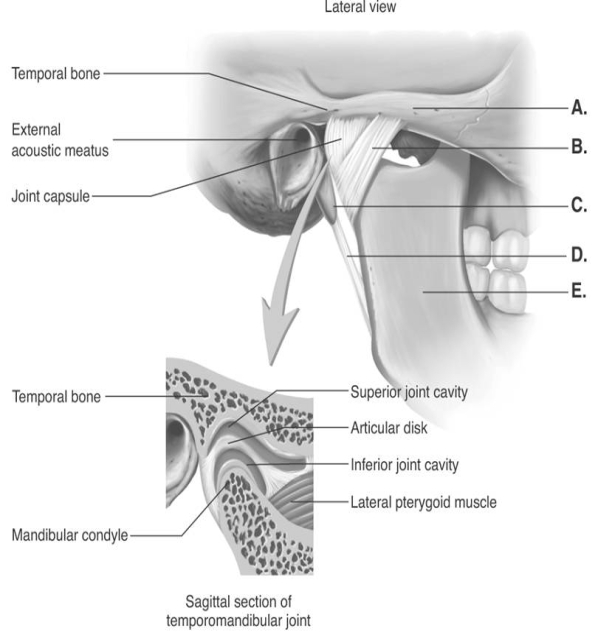 -The figure illustrates structures in the right temporomandibular joint (lateral view) . What does "A" represent?
-The figure illustrates structures in the right temporomandibular joint (lateral view) . What does "A" represent?
A) lateral ligament
B) mandible
C) zygomatic arch
D) styloid process
E) stylomandibular ligament
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A joint that has no joint cavity and exhibits little or no movement would be classified as a
A) fibrous joint.
B) synovial joint.
C) complex joint.
D) cartilaginous joint.
E) partial joint.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the TMJ joint, the mandible articulates with the
A) temporal bone.
B) maxilla.
C) zygomatic bone.
D) tympanic bone.
E) parietal bone.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 119
Related Exams