A) digestion of unneeded cell organelles
B) recognition of bacterial cells by the immune system
C) transport of products from the nucleus to the endoplasmic reticulum
D) cell metabolism
E) detoxification
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
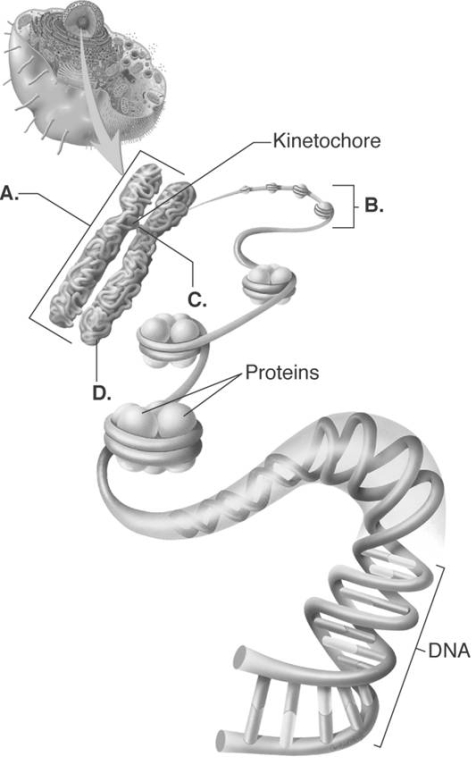 -Answer these questions about chromosome structure. What does "A" represent?
-Answer these questions about chromosome structure. What does "A" represent?
A) chromatid
B) proteins
C) chromosome
D) centromere
E) chromatin
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In _______, ions or molecules move in opposite directions.
A) symport
B) uniport
C) antiport
D) comport
E) ionport
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The environment outside the plasma membrane is most appropriately referred to as
A) intracellular.
B) extracellular.
C) multicellular.
D) centrocellular.
E) None of these choices are correct.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is the condition of the RBC in solution "B"?
-Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is the condition of the RBC in solution "B"?
A) hypotonic solution
B) hypertonic solution
C) isotonic solution
D) hemolyzed
E) crenated
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events occurs during anaphase?
A) Chromatin strands condense to form chromosomes.
B) Chromosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell.
C) Spindle fibers are formed.
D) The nuclear envelope degenerates.
E) Cytokinesis completes.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which transport process requires a carrier molecule but does not use cellular energy?
A) active transport
B) diffusion
C) endocytosis
D) facilitated diffusion
E) osmosis
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The leading strand of DNA is formed as
A) short segments called Okazaki fragments.
B) a continuous strand, adding to the 3´ end.
C) a continuous strand, adding to the 5´ end.
D) a template.
E) soon as the lagging strand is formed.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you compare a cell with a manufacturing plant that exports goods, the cell's _____ could be compared to the manufacturing plant's shipping department.
A) nucleus
B) lysosome
C) Golgi apparatus
D) endoplasmic reticulum
E) ribosome
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The shaft of a flagellum contains _____________ microtubule doublets around its periphery.
A) 2
B) 2 + 9
C) 9
D) 2+7
E) 7
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are consistent with facilitated diffusion? (1) movement is against a concentration gradient (2) movement is with a concentration gradient (3) involves a carrier molecule (4) involves cotransport (5) involves counter transport (6) exhibits competition and saturation
A) 1, 2, 4, 5, 6
B) 2, 3, 6
C) 2, 3, 5, 6
D) 1, 3, 4, 5, 6
E) 2, 3, 4, 6
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell with abundant peroxisomes would most likely be involved in
A) secretion.
B) storage of glycogen.
C) detoxification activities.
D) cellular communication.
E) protein synthesis.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cancer that is able to spread and become worse is called
A) metastasis
B) malignant
C) sarcoma
D) benign
E) carcinoma
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aroma of cookies baking in the kitchen reaches you in the living room. The distribution of this odor throughout the house is an example of
A) active transport.
B) dialysis.
C) osmosis.
D) filtration.
E) diffusion.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Organelles
A) are extracellular structures.
B) are unspecialized portions of a cell.
C) generally lack membranes.
D) vary in number and type depending on cell function.
E) are structural, but not functional parts of the cell.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
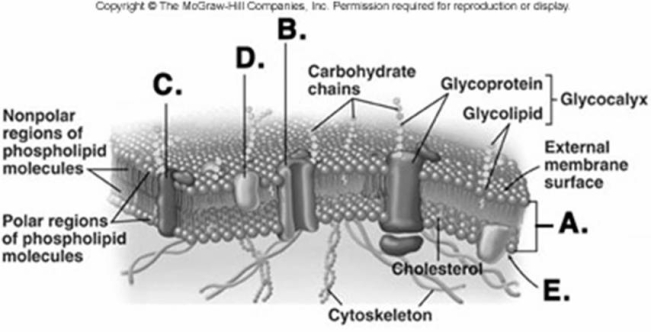 -What structure does "C" represent on the diagram of the plasma membrane?
-What structure does "C" represent on the diagram of the plasma membrane?
A) membrane channel protein
B) phospholipid bilayer
C) internal membrane surface
D) peripheral protein
E) integral protein
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following activities is associated with lysosomes?
A) exocytosis
B) intracellular support
C) destruction of nonfunctional organelles
D) energy production
E) endocytosis
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The lower limit of resolution of a light microscope is
A) 100 m
B) 0.1 m
C) 10 m
D) 0.01 m
E) 1.0 m
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will increase the rate of diffusion?
A) an increase in the viscosity of the solvent
B) an increase in the temperature
C) an increase in the molecular weight of the diffusing particles
D) an increase in the distance the molecules have to travel
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true of a gene?
A) It is all the triplets needed to make a functional RNA or protein.
B) It is a segment of a DNA molecule.
C) Each chromosome contains one gene.
D) It is the functional unit of heredity.
E) All of these are true of a gene.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 211
Related Exams