A) chorion
B) placenta
C) yolk sac
D) amnion
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is brain growth in humans different from other mammals?
A) In humans brain growth is complete by the third trimester.
B) In humans brain growth stops at birth.
C) Human growth is not allometric.
D) In humans brain growth continues after birth.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In this diagram, which of the following numbers represents the actual event of egg activation? 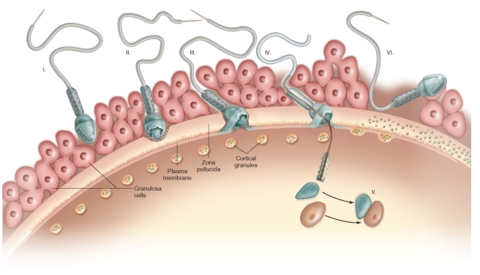
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In blind cave fish, eyes do not form.However, transplantation of the lens from a closely-related aboveground fish into the optic cup of the cave fish induces eye development.What does this suggest about the loss of vision in the cave fish?
A) Primary induction of the eye fails in the cave fish because the lens lacks some critical signal.
B) Secondary induction of the eye fails in the cave fish because the lens lacks some critical signal.
C) Primary induction of the eye fails in the cave fish because the optic cup lacks the ability to receive some critical signal.
D) Secondary induction of the eye fails in the cave fish because the optic cup lacks the ability to receive some critical signal.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What pattern of cleavage is characteristic of mammals?
A) holoblastic cleavage with eggs containing little or no yolk
B) some yolk, and cleavage resulting in vegetal and animal poles
C) meroblastic cleavage with eggs containing almost entirely yolk
D) holoblastic cleavage with eggs containing very little yolk, but with the inner cell mass concentrated at one pole
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following activates the egg?
A) entrance of sperm into the zona pellucida
B) contact of sperm with the outside of the zona pellucida
C) contact of sperm with the vitelline envelope
D) fusion of sperm and egg membranes
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would result if an error inside gastrulation caused too few cells inside the archenteron?
A) Too little endoderm, resulting in missing gut and organs
B) Too little ectoderm, resulting in missing nervous system or skin
C) Problems in muscle development
D) Too little protoderm, resulting in missing organs
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the placenta is delivered, what event allows secretion of prolactin and milk production?
A) a surge of adrenaline and endorphins
B) sudden drop in progesterone and estradiol
C) gradual drop in oxytocin
D) sudden rise in FSH and LH
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In human females, what process causes milk production?
A) Stimulation of the alveoli of the mammary glands by prolactin from the anterior pituitary gland.
B) Stimulation of the alveoli of the mammary glands by oxytocin from the anterior pituitary gland.
C) Stimulation of the alveoli of the mammary glands by prolactin from the posterior pituitary gland.
D) Stimulation of the alveoli of the mammary glands by oxytocin from the posterior pituitary gland.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the two components of the human placenta?
A) chorionic frondosum and chorionic villus
B) chorionic frondosum and decidua basalis
C) decidua basalis and chorionic villus
D) chorionic villus and endometrium
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
400 micrograms a day of folic acid are recommended for all women of child-bearing age.Folic acid helps prevent neural tube defects in the first weeks of pregnancy, before most women even realize they are pregnant (and almost half of pregnancies in the U.S.are unintended) .Knowing that folic acid promotes proper neural tube closure, which disease can be prevented by this supplement?
A) Spina bifida -- the vertebrae are unfused and may allow the spinal cord to protrude outside the body
B) Horseshoe kidney -- the two kidneys are fused together across the midline
C) Esophageal atresia -- the esophagous ends in a pouch, unconnected to the stomach
D) Chronic otitis media -- frequent ear infections that can result from blocked eustachian tubes
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are studying the development of a poorly-understood species at the 8-cell stage.You use a laser to zap away a certain one of the eight cells, and discover that part of the gut is missing once the embryos finish development.Your colleague, who is working on a different species, uses the laser to blast away one of the cells in her embryos, zapping each of the possible cells in a set of eight experiments.However, when the embryos finish development, every one is perfectly normal! What can you conclude about the two species?
A) The first species has regulative development, the second has non-regulative development.
B) The first species has non-regulative development, the second has regulative development.
C) Both species have regulative development.
D) Both species have non-regulative development.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would result if too many cells left the surface of the embryo to move inside during gastruation?
A) Too little endoderm, resulting in missing gut and organs
B) Too little ectoderm, resulting in missing nervous system or skin
C) Problems in muscle development
D) Too little protoderm, resulting in missing organs
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would result if a defect in gastrulation caused too little mesoderm inside the embryo?
A) Too little endoderm, resulting in missing gut and organs
B) Too little ectoderm, resulting in missing nervous system or skin
C) Problems in muscle development
D) Too little protoderm, resulting in missing organs
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would be the result of a mutation that reduces the amount of acrosomal enzymes?
A) Male infertility due to inability of the sperm to tunnel through the blastula.
B) Male infertility due to inability of the sperm to tunnel through the zona pellucida.
C) Female infertility due to blockage of sperm from tunneling through the allantois.
D) Female infertility due to blockage of sperm from tunneling through the archenteron.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What prevents menstruation from occurring in the 10th week when the corpus luteum regresses?
A) The follicle takes over secretion of hCG.
B) The follicle takes over secretion of estradiol and progesterone.
C) The placenta takes over secretion of estradiol and progesterone.
D) The cervix takes over secretion of oxytocin and prostaglandins.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Working in an experimental fertility clinic, a researcher removes one cell from an 8-cell stage chimpanzee embryo.What is the likely result?
A) Both the cell and the blastula will die.
B) All the cells are already committed and therefore are not viable.
C) The embryo from which the cell was removed still remains viable and can form a normal chimp.
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The snakes include some rather short and some incredibly long species, with a variation from about 100 to over 300 vertebrae.What developmental mechanism is the best candidate for changing the number of vertebrae in evolution?
A) Changes in genes that lay down extracellular matrix in bone
B) Changes in genes necessary for neural crest development
C) Changes in genes that control mitosis
D) Changes in the somitogenesis clock
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What human organ is formed from two genetically-different tissues?
A) neural crest
B) neural tube
C) placenta
D) uterus
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following leads to the occurrence of vertebrate sense organs?
A) both adrenal medullary cells and sympathetic neurons derive from the neural crest
B) neural crest cells form both neurons that carry messages and cartilaginous bars
C) the neural crest and associated sensory ganglia
D) formation of the endoderm
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 55
Related Exams