A) the movement of water between the oceans and the land
B) how precipitation ends up in rivers or groundwater
C) how weathering causes the seas to become saltier
D) all of these
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens when rocks oxidize near Earth's surface?
A) minerals in the rock release oxygen that can break down adjacent rocks
B) oxygen combines with water to create weak acids that weather rocks
C) minerals, especially those with iron, combine with oxygen
D) oxygen combines with silica to make quartz
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are problems related to soil?
A) individual grains lose contact with one another as water squeezes between them
B) certain clay minerals increase in volume when they become wet
C) soils that do not compact uniformly because of varying amounts of clay
D) erosion due to loss of plant cover, such as from overgrazing
E) all of these
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a common trigger for slope failure?
A) adding water to a slope
B) volcanic eruption
C) shaking during an earthquake
D) oversteepening of cliffs or hillslopes during road construction
E) all of these are common triggers for slope failure
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about how weathering affects fractured rocks?
A) Weathering affects rocks from the outside in, forming an outer weathered zone or rind.
B) Weathering attacks corners from three sides and so these are preferentially removed.
C) Preferential weathering along fractures can cause blocks to become rounded.
D) D. All of these.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors does NOT control the stability of a slope?
A) the angle of repose for intact bedrock
B) whether the slope is rock or soil
C) the amount of water in the soil
D) the orientation of fractures, cleavage, and bedding
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aside from limestone, which other kinds of rock types produce karst terrain?
A) evaporite rocks such as salt and gypsum
B) granite
C) sandstone
D) shale
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an expression of the angle of repose?
A) talus slope
B) some slopes of sand dunes
C) angle of slopes on scoria cones
D) all of these
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of slope failure is shown in this figure? 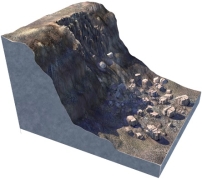
A) rotational slide
B) creep
C) earth flow
D) debris flow
E) rock fall
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the main hazard for areas along the river terrace?
A) shrinking and swelling of clays
B) slow movement of material downslope
C) rock falls
D) debris flows that carry large blocks from the volcano
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of slope failure shown in this photograph is: 
A) creep
B) a rock slide
C) a debris avalanche
D) a debris flow
E) all of these
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following generally is true about caves formed by dissolution?
A) acidic waters dissolve feldspar in granite, producing clay
B) groundwater removed material from limestone
C) hot geothermal waters introduce acids into shallow rocks
D) carbon dioxide rises from depth and dissolves calcite and clay
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the main process by which soils form?
A) deposition of silt on a floodplain
B) deposition of silt by the wind
C) weathering
D) erosion
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As illustrated in this figure, which of the following is NOT potential trigger for slope failure? 
A) precipitation that can saturate and weaken sediment
B) undercutting of steep slopes by roads and rivers
C) shaking during an earthquake
D) shaking of slopes and melting of snow during volcanic eruptions
E) all of these are illustrated
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has the lowest potential for landslides?
A) Pacific Northwest
B) southern California
C) bluffs along rivers in the central U.S.
D) Florida
E) Appalachian Mountains
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People reshape steep slopes, a practice called terracing, in order to: 
A) help capture and retain rainfall
B) provide a level place on which to farm
C) promote soil formation
D) protect soil from erosion
E) all of these
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors caused some high peaks of the Cascade Mountains of the Pacific Northwest to have high potential for slope failure?
A) they are volcanoes with steep slopes
B) they experience heavy rainfall
C) they may contain loose volcanic ash and other volcanic materials
D) all of these
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the main force involved in the stability of slopes?
A) water pressure
B) sunlight
C) wind
D) gravity
E) radioactivity decay
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following might indicate that slopes adjacent to this landslide might fail? 
A) they have the same steepness as the slope that failed
B) they appear to have a similar geology setting
C) one part of the slope has already failed
D) all of these
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of slope failure is shown in this figure? 
A) rotational slide
B) creep
C) debris slide
D) debris flow
E) rock fall
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 92
Related Exams