A) The sediments become compacted.
B) The sediments remain suspended.
C) The sediments move into the cone of depression.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a feature that commonly forms where limestone has been dissolved?
A) sinkhole
B) karst topography
C) cave
D) all of these
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The permeability of a material refers to:
A) the volume of air space in a material
B) a meandering stream's movement across the underlying bedrock
C) the ease with which a stream erodes material
D) the ability of water to flow through a material
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events is most like the formation of a cloud?
A) water running off a roof
B) water forming on a cold object on a hot, humid summer day
C) water entering the air from the leaves of growing plants
D) water moving downward into the soil after a summer rain storm
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cone of depression can form if:
A) groundwater is overpumped from an aquifer
B) limestone caverns collapse
C) an artesian well goes dry
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where on this cross section would water at the surface infiltrate to become groundwater? 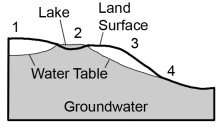
A) 1, 2, and 3
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 only
E) 4 only
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A part of a steam that receives water from the inflow of ground water is called a: 
A) gaining stream
B) losing stream
C) hydraulic gradient
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most similar in volume to an acre-foot of water?
A) 1,000 gallons
B) an acre covered to a depth of 3 feet 1 meter)
C) most of a football field covered to a depth of 1 foot
D) a square mile of land covered to a depth of 3 feet 1 meter)
E) 20 million gallons
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The first step in constructing a contour map of a water table is to:
A) collect and plot the elevations of the water table in all available wells in an area
B) collect water quality data and plot it with all available wells in the area
C) determine the amount of water present in the subsurface
D) calculate the age of the water in the water table
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following materials has high porosity and high permeability?
A) unfractured granite
B) well-sorted gravel
C) compacted clay
D) uncompacted clay
E) poorly sorted sand, silt, and clay
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What might happen to a losing stream as the water passes from flowing over hard, impermeable rocks to flowing over more permeable rocks?
A) The stream will lose more water to the subsurface and might disappear.
B) The stream will gain water and flow faster.
C) No change will occur in the stream flow.
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This cross section shows the location of a septic tank with harmful bacteria and 5 wells. Which well is least likely to become contaminated?
A) well A
B) well B
C) well C
D) well D
E) well E![]()
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following energy sources drives the hydrologic cycle?
A) internal heat energy
B) river flow
C) wind energy
D) solar energy
E) gravity
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true about the water table?
A) the water table is right at the land surface in swamps
B) the water table is generally horizontal
C) the water table is above the land surface in lakes
D) overpumping can change the slope of the water table
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following materials has moderate to high porosity but low permeability?
A) fractured sandstone
B) uncompacted clays
C) well-sorted gravel
D) well-sorted sand
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a material that holds groundwater, porosity:
A) controls the amount of water that can be stored
B) determines the composition of the cement between grains and clasts
C) does not depend on the size and shape of grains and clasts
D) is constant from one type of material to another
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which two uses consume most freshwater in the United States?
A) drinking water and showering
B) mining and raising livestock
C) irrigation and drinking water
D) mining and industrial use
E) thermoelectric power and irrigation
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each number on this figure refers to a location with groundwater in a subsurface material that is consistent in character across the entire figure. Of these locations, which one would have groundwater flowing to the left? 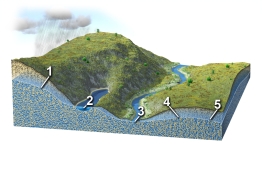
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following generally is true about caves formed by dissolution?
A) acidic waters dissolve feldspar in granite, producing clay
B) groundwater removed material from limestone
C) hot geothermal waters introduce acids into shallow rocks
D) carbon dioxide rises from depth and dissolves calcite and clay
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following materials probably has the highest porosity?
A) poorly sorted sediment
B) sediment composed only of rounded cobbles that rest directly on one another
C) a mixture of sand, silt, and clay
D) a coarse-grained granite
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 142
Related Exams