A) free rider problem
B) collective action problem
C) moral hazard
D) societal well-being problem
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to proportional-representation systems, two-party systems are thought to:
A) lead to more diverse views in the policy process.
B) offer a wider variety of platforms among which voters can choose.
C) create unwieldy combinations of policies within one platform.
D) be much less efficient and lead to very few compromises when voting.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At its extreme, the use of the powers of government by public officials to achieve personal gains is:
A) collective action.
B) corruption.
C) bribery.
D) a moral hazard.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose everyone in a town votes that they prefer improved public transportation systems over new public parks. According to the criteria of ________________, that preference should not change even if a third option, like a new public zoo, is introduced.
A) transitivity
B) no dictator
C) unanimity
D) independence of irrelevant alternatives
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown displays voters' preferences in an election.
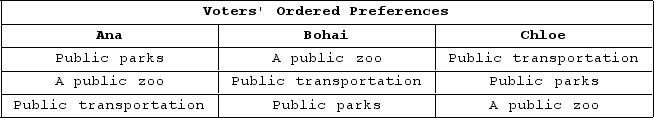 If a pairwise majority vote is held, and Bohai sets the agenda for votes, which pair will he put up for vote first?
If a pairwise majority vote is held, and Bohai sets the agenda for votes, which pair will he put up for vote first?
A) A public zoo and public parks
B) Public transportation and a public zoo
C) Public parks and public transportation
D) Any pair, as it will not affect the outcome of the voting.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mail-in ballots are designed to:
A) increase your ability to fulfill your civic duty.
B) increase the utility derived from voting.
C) decrease the costs associated with voting.
D) increase the accuracy of the voting process.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown displays voters' preferences in an election.
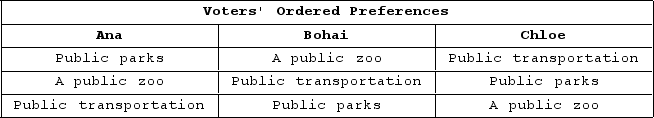 If a pairwise majority vote is held, and the first pair to be voted on is a public zoo and public transportation, which voter(s) will be happiest with the outcome?
If a pairwise majority vote is held, and the first pair to be voted on is a public zoo and public transportation, which voter(s) will be happiest with the outcome?
A) Bohai
B) Chloe
C) Ana
D) Ana and Bohai
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An ideal voting system will not function if a _______ is present who has the power to enact his or her own preferences.
A) congress
B) representative
C) consul
D) dictator
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Commentators on the presidential election between Bush and Gore in 2000 believe that the presence of Nader, a third-party candidate:
A) drew votes away from Gore, causing him to lose the election.
B) pushed more people to vote for Bush, causing him to win the election.
C) drew votes away from Bush, causing him to lose the election.
D) drew votes away from Bush, causing him to win the election.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The time and money it takes to organize a group or a campaign and to get people's attention:
A) is the cost of collective action.
B) is the reason why collective action does not occur in the real world.
C) is a concentrated cost to individuals but a diffuse cost to society.
D) leads to corruption and rent-seeking behavior.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount of corruption that occurs in a government is hard to measure because:
A) its costs are mostly indirect and nearly impossible to measure.
B) it is illegal, and therefore hidden.
C) the benefits often go to a small number of people and distort the reality.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _______ theorem suggests that politicians maximize their votes by taking the policy position preferred by the median voter, under certain conditions?
A) average voter
B) mid-voter
C) median-voter
D) moderate voter
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pairwise majority voting _______ of the criteria of an ideal voting system.
A) fails to meet one
B) fails to meet two
C) fails to meet all
D) meets all
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pairwise majority voting fails to meet which of the following criteria of an ideal voting system?
A) Transitivity
B) Independence of irrelevant alternatives and transitivity
C) No dictator and transitivity
D) No dictator and independence of irrelevant alternatives
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Poll taxes are:
A) a way to disenfranchise the poor.
B) a tax that must be paid in order to cast a vote.
C) used to disenfranchise certain groups even when the right to vote exists.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If we think of good governance as a public good created by well-informed voters, we can predict that it will be:
A) oversupplied.
B) undersupplied.
C) in market equilibrium, if left unchecked.
D) in market equilibrium, despite market interference.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true of term limits on political offices?
A) They prevent officials from holding office for longer than a certain amount of time.
B) They discourage corruption by ensuring that one person isn't allowed to hold onto power for too long.
C) They can encourage corruption by placing an official in power with no incentive to answer to the constituency.
D) They encourage people to run for multiple different political offices.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a vote is taken in a small town of 11 people to determine how much of the budget should go toward education spending. Five individuals vote for 10 percent, five others vote for 80 percent and one person votes for 25 percent. According to the median-voter theorem, the chosen amount to spend on education will be _______ percent of the budget.
A) 10
B) 80
C) 45
D) 25
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the liberum veto is used in a policy-making setting, it means:
A) complete consensus is needed for legislation to pass.
B) policies can easily be halted, because only one person needs to be bribed to stop them.
C) the government is an easy target for corruption.
D) All of these are true.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When people are reluctant to voluntarily pay for goods and services that provide benefits for everyone, including those who don't pay, _______ exists.
A) the drop in the bucket hypothesis
B) rational ignorance
C) moral hazard
D) the free rider problem
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 113
Related Exams