A) The equilibrium quantity will be too high.
B) The outcome will not maximize surplus.
C) The outcome will still be efficient.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a positive externality is present in a market, consumers will purchase _______ the socially optimal quantity.
A) more than
B) the same amount as
C) zero, unlike
D) less than
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Latoya and Maggie are roommates. Maggie likes to play music in their dorm room every evening. Tonight, Latoya needs to study for her economics exam and would prefer that Maggie not play music. Latoya values silence at $50. Maggie values her music at $20. Assume the roommates can bargain with zero transactions costs. If the dorm rules are such that Maggie is allowed to play music whenever she likes, which of the following is true?
A) Maggie could offer to pay Latoya $20 in exchange for playing her music, an offer that Latoya would accept.
B) Maggie will not be able to offer any amount high enough to convince Latoya to allow music.
C) Maggie and Latoya will not be able to reach an agreement that results in Maggie turning off her music for the evening.
D) Latoya could offer to pay Maggie $25 in exchange for Maggie turning off her music, an offer that Maggie would accept.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The idea that individuals can reach an efficient equilibrium through private trades, even in the presence of an externality, is called:
A) market failure.
B) trade quotas.
C) the Coase theorem.
D) the invisible hand.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Latoya and Maggie are roommates. Maggie likes to play music in their dorm room every evening. Tonight, Latoya needs to study for her economics exam and would prefer that Maggie not play music. Latoya values silence at $50. Maggie values her music at $20. Assume the roommates can bargain with zero transactions costs. Which of the following is true?
A) It is efficient for Maggie to play her music.
B) Maggie and Latoya will not be able to reach efficiency in this situation.
C) The university should offer a subsidy for noise-cancelling headphones.
D) It is efficient for Maggie to refrain from playing music tonight.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Markets fail to maximize total surplus when:
A) individual choices impose costs or benefits on others.
B) society's choices impose costs or benefits on other societies.
C) all costs and benefits are received by participants in transactions.
D) producer surplus is not exactly equal to consumer surplus.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a production process causes a negative externality, then the social cost of production will be _______ the private cost of production.
A) larger than
B) the same as
C) smaller than
D) zero, unlike
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a Pigovian tax is levied on a market, price _______ and quantity _______ to the efficient level.
A) increases; decreases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tax on cigarettes:
A) increases total surplus.
B) increases efficiency in the market.
C) increases both total surplus and efficiency in the market.
D) always reduces surplus and efficiency in the market.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays a market with an externality. 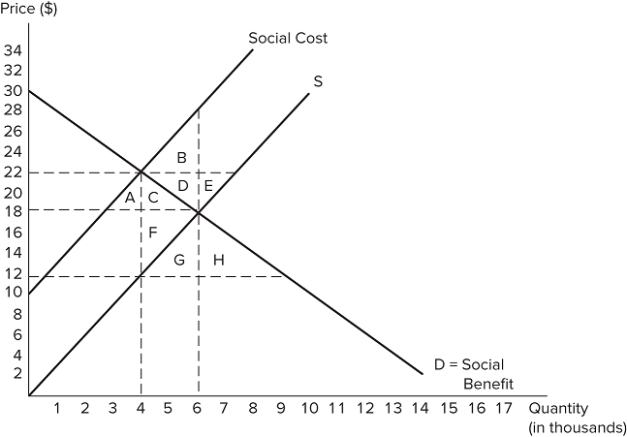 Which areas represent deadweight loss?
Which areas represent deadweight loss?
A) A + C
B) B + D
C) C + F
D) D + E
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a negative externality is present in a market, consumers will purchase _______ the socially optimal quantity.
A) zero, unlike
B) more than
C) the same amount as
D) less than
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a positive externality exists in a market, the distribution of surplus received from a subsidy depends on:
A) how the subsidy is distributed among those affected by the externality.
B) whether those who are affected by the externality receive its true value.
C) where the government obtains the money it uses to pay for the subsidy.
D) None of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who is affected when a Pigovian tax is imposed on a market with a negative production externality?
A) Producers
B) Consumers
C) Those affected by the externality
D) All of these groups are affected when a Pigovian tax is imposed.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about a Pigovian tax is true? If the amount of the tax is equal to the external cost, deadweight loss will be zero. The tax must be placed on producers. The tax moves the market quantity closer to the efficient quantity.
A) I only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If it is possible to eliminate the problems created by externalities, why do they persist?
A) Correcting externalities always reduces total surplus.
B) It is difficult to measure external benefits and costs.
C) The costs of imposing taxes and subsidies generally exceed the benefits.
D) None of these are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The biggest difference between using a Pigovian tax or a tradable allowance to correct for a negative externality is:
A) the government collects revenues from a Pigovian tax, whereas a tradable allowance allows private parties to trade quota rights on their own.
B) a Pigovian tax creates an efficient outcome, while a tradable allowance does not.
C) a Pigovian tax maximizes total surplus, whereas a tradable allowance does not.
D) All of these are differences between Pigovian taxes and tradeable allowances.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Pigovian tax is intended to:
A) counter the effect of a negative externality.
B) decrease efficiency in a market.
C) decrease total surplus in a market.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a market is fully corrected for externalities, it:
A) is equitable.
B) maximizes surplus.
C) makes everyone in society better off.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a negative consumption externality is present in a market, total surplus will be _______ if buyers only consider _______ costs.
A) higher; private
B) lower; private
C) lower; social
D) unchanged; social
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a Pigovian tax is levied on consumers, the demand curve will shift straight _______ and the equilibrium quantity will _______.
A) up; decrease
B) down; decrease
C) down; increase
D) up; increase
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 131
Related Exams