A) 56 kN
B) 48 kN
C) 52 kN
D) 44 kN
E) 36 kN
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2000-kg truck travelling at a speed of 6.0 m/s makes a 90 turn in a time of 4.0 s and emerges from this turn with a speed of 4.0 m/s. What is the magnitude of the average resultant force on the truck during this turn?
A) 4.0 kN
B) 5.0 kN
C) 3.6 kN
D) 6.4 kN
E) 0.67 kN
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A steel ball bearing of mass m1 and speed of magnitude v1 has a head-on elastic collision with a steel ball bearing of mass m2 at rest. Rank the speed v1 of m1 relative to v2, the magnitude of the speed of m2, after the collision when: i) m1 > m2; ii) m1 = m2; and iii) m1 < m2.
A) v1 < v2; v1 < v2; v1 < v2
B) v1 < v2; v1 = v2; v1 > v2
C) v1 < v2; v1 > v2; v1 > v2
D) v1 > v2; v1 = v2; v1 < v2
E) v1 > v2; v1 > v2; v1 > v2
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two 0.20-kg balls, moving at 4 m/s east, strike a wall. Ball A bounces backwards at the same speed. Ball B stops. Which statement correctly describes the change in momentum of the two balls?
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) B = A.
E) B > A.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the rate of burn and the exhaust velocity are constant, a rocket ascends with:
A) decreasing acceleration.
B) decreasing velocity.
C) constant velocity.
D) constant acceleration.
E) increasing acceleration.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.0-kg object moving 3.0 m/s strikes a 1.0-kg object initially at rest. Immediately after the collision, the 2.0-kg object has a velocity of 1.5 m/s directed 30 from its initial direction of motion. What is the x component of the velocity of the 1.0-kg object just after the collision?
A) 3.7 m/s
B) 3.4 m/s
C) 1.5 m/s
D) 2.4 m/s
E) 4.1 m/s
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rocket engine consumes 450 kg of fuel per minute. If the exhaust speed of the ejected fuel is 5.2 km/s, what is the thrust of the rocket?
A) 42 kN
B) 39 kN
C) 45 kN
D) 48 kN
E) 35 kN
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1.6-kg ball is attached to the end of a 0.40-m string to form a pendulum. This pendulum is released from rest with the string horizontal. At the lowest point of its swing, when it is moving horizontally, the ball collides with a 0.80-kg block initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface. The speed of the block just after the collision is 3.0 m/s. What is the speed of the ball just after the collision?
A) 1.7 m/s
B) 1.1 m/s
C) 1.5 m/s
D) 1.3 m/s
E) 2.1 m/s
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 6.0-kg object, initially at rest in free space, 'explodes' into three segments of equal mass. Two of these segments are observed to be moving with equal speeds of 20 m/s with an angle of 60 between their directions of motion. How much kinetic energy is released in this explosion?
A) 2.4 kJ
B) 2.9 kJ
C) 2.0 kJ
D) 3.4 kJ
E) 1.2 kJ
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 10-g bullet moving 1000 m/s strikes and passes through a 2.0-kg block initially at rest, as shown. The bullet emerges from the block with a speed of 400 m/s. To what maximum height will the block rise above its initial position? 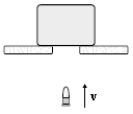
A) 78 cm
B) 66 cm
C) 56 cm
D) 46 cm
E) 37 cm
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1.5-kg playground ball is moving with a velocity of 3.0 m/s directed 30 below the horizontal just before it strikes a horizontal surface. The ball leaves this surface 0.50 s later with a velocity of 2.0 m/s directed 60 above the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the average resultant force on the ball?
A) 14 N
B) 11 N
C) 18 N
D) 22 N
E) 3.0 N
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At an instant when a particle of mass 50 g has an acceleration of 80 m/s2 in the positive x direction, a 75-g particle has an acceleration of 40 m/s2 in the positive y direction. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the centre of mass of this two-particle system at this instant?
A) 60 m/s2
B) 56 m/s2
C) 40 m/s2
D) 50 m/s2
E) 46 m/s2
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An 8.0-kg object moving 4.0 m/s in the positive x direction has a one-dimensional collision with a 2.0-kg object moving 3.0 m/s in the opposite direction. The final velocity of the 8.0-kg object is 2.0 m/s in the positive x direction. What is the total kinetic energy of the two-mass system after the collision?
A) 32 J
B) 52 J
C) 41 J
D) 25 J
E) 29 J
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.0-kg object moving with a velocity of 5.0 m/s in the positive x direction strikes and sticks to a 3.0-kg object moving with a speed of 2.0 m/s in the same direction. How much kinetic energy is lost in this collision?
A) 2.4 J
B) 9.6 J
C) 5.4 J
D) 0.6 J
E) 6.0 J
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Car A rear ends Car B, which has twice the mass of A, on an icy road at a speed low enough so that the collision is essentially elastic. Car B is stopped at a light when it is struck. Car A has mass m and speed v before the collision. After the collision
A) each car has half the momentum.
B) car A stops and car B has momentum mv.
C) car A stops and car B has momentum 2mv.
D) the momentum of car B is four times as great in magnitude as that of car A.
E) each car has half of the kinetic energy.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The speed of a 2.0-kg object changes from 30 m/s to 40 m/s during a 5.0-s time interval. During this same time interval, the velocity of the object changes its direction by 90 . What is the magnitude of the average total force acting on the object during this time interval?
A) 30 N
B) 20 N
C) 40 N
D) 50 N
E) 6.0 N
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A catapult fires an 800-kg rock with an initial velocity of 100 m/s at a 40 angle to the ground. The magnitude of the horizontal impulse the catapult receives from the rock is:
A) 5.1* 104 N s.
B) 6.1 * 104 N s.
C) 8.0 * 104 N s.
D) 5.0 * 105 N s.
E) 6.0 * 105 N s.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two bodies of equal mass m collide and stick together. The quantities that always have equal magnitude for both masses during the collision are:
A) their changes in momentum.
B) the force each exerts on the other.
C) their changes in kinetic energy.
D) all of the above.
E) only (a) and (b) above.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two bodies with masses m1 and m2 are both moving east with velocities of magnitudes v1 and v2, where v1 is less than v2. The magnitude of the velocity of the centre of mass of this system of two bodies is:
A) less than v1.
B) equal to v1.
C) equal to the average of v1 and v2.
D) greater than v1 and less than v2.
E) greater than v2.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 12-g bullet moving horizontally strikes and remains in a 3.0-kg block initially at rest on the edge of a table. The block, which is initially 80 cm above the floor, strikes the floor a horizontal distance of 120 cm from its initial position. What was the initial speed of the bullet?
A) 0.68 km/s
B) 0.75 km/s
C) 0.81 km/s
D) 0.87 km/s
E) 0.41 km/s
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 47
Related Exams