A) intraspecific competition
B) predation
C) prey availability
D) soil type
E) sunlight
F) temperature
G) water
I) E) and F)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This summer, you are returning to the research station in Costa Rica to follow up on the population of butterflies you have been studying. You are disappointed to find that there are fewer this year than last. In fact, at dinner your friends studying frogs and birds are complaining about the same thing. What type of influence do you suspect?
A) a density-independent effect like an introduced predator
B) a density-dependent effect like environmental disruption
C) a density-independent effect like environmental disruption
D) a density-dependent effect like an introduced predator
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many organisms have adaptations to avoid freezing temperatures, including behaviors like migration, features like thick fur, and molecular features like antifreeze molecules. However, some organisms have a adaptation called ice nucleation, in which special proteins help ice crystals to form at warmer temperatures. What organism would be most likely to benefit from such an adaptation?
A) a bacterial pathogen that feeds off damaged plants
B) a saltwater fish that lives in coral reefs
C) a bird species that migrates long distances
D) a species of yeast used in brewing beer
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An underwater volcano has erupted, and as the lava cools a new island has formed. Which types of animal species are likely to be among the first to colonize the island?
A) annelids
B) bats
C) birds
D) insects
E) snails
F) snakes
G) tapirs
H) tortoises
J) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the late 1800s, cattle egrets arrived in South America from Africa and began to colonize. Their range has expanded dramatically over the years. Why were they able to do this?
A) The habitats that they left in Africa were not suitable for any further colonization; thus, they were forced to emigrate.
B) The habitats that they encountered in South America were suitable to them and unoccupied.
C) There were abundant cattle for the birds to gather around in South America; furthermore, various animals that the egrets had lived around in Africa had become quite scarce because of over hunting and poaching, causing the birds to extend their range.
D) The food resources in South America were far superior to those in Africa, allowing the egrets more opportunity to grow and reproduce and ultimately expand their range.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A graduate student is studying the feeding behavior of a small octopus that must be laboriously collected from the shores of a remote island. Her intern wishes to do experiments to look at the octopus's mating behavior. Why might the graduate student veto this idea?
A) The octopus has semelparous reproduction, and will eat its mate.
B) The octopus has iteroparous reproduction, and will eat its mate.
C) The octopus has semelparous reproduction, and will die after laying one batch of eggs.
D) The octopus has iteroparous reproduction, and will die after laying one batch of eggs.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A farmer's land includes a wilderness area that is home to an endangered species of bird. He wants to sell the land to a developer, and you have been hired to evaluate the environmental concerns. "This little patch of land is not crucial for the bird species!" the farmer says, "In fact, my land is surrounded by several other wilderness patches that also have that bird." You reply: "It is possible that your land acts as the ____________ and the other areas are ___________ . If that's the case, development would be devastating to the population."
A) sink; sources
B) source; sinks
C) population; metapopulation
D) metapopulation; population
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two populations have very similar birth rates and death rates, but the change in the growth of the populations is quite different. What other factors might account for the difference? (Check all that apply.)
A) age structure
B) primary food source
C) generation time
D) immigration
E) sex ratio
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure included shows the body temperature of lizards versus air temperature in two different habitats-open and shaded forest. Which one of the following conclusions is best supported by these data. 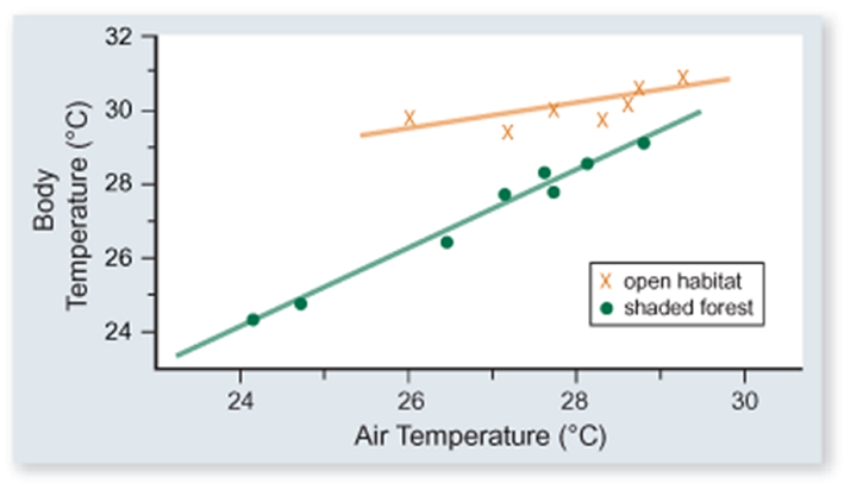
A) Lizards are more active in open habitats.
B) Lizards sunbathe more in open habitats.
C) Lizards in shaded forest habitats eat more to maintain their temperature.
D) The body temperature of lizards is more constant in open than in shaded forest habitats.
E) The negative effect of air temperature on body temperature is less in shaded forest habitats because the temperature varies less there.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A small group of mice were released on an island. The island previously had no mice on it, but had abundant food and no predators. After several years of growth, the size of the new island population stabilizes. However, at this point a hurricane drastically reduces the population. How would you describe the situation?
A) The biotic potential of the population has been reduced.
B) The new population size is a result of density-dependent regulation.
C) The new population size is a result of density-independent regulation.
D) The island mouse population can now act as a sink metapopulation.
E) The island mouse population can now act as a source metapopulation.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describe density-dependent factors?
A) They act to regulate population growth.
B) They are especially important in K-selected populations.
C) They can affect growth rates but not population size.
D) They can affect birth rates or death rates.
E) They do not involve biological interactions.
F) One example would be intraspecific competition for resources.
H) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are three aspects of entire populations that are important and often studied. Select the best choice from the ones listed.
A) a population's range, the dispersal of individuals within the range, and the size that the population attains
B) a population's range, the amount of food available within the range, and the size that the population attains
C) a population's range, the parental care received by each offspring within the population, and the size that the population attains
D) a population's range, the size home range of an individual in the population, and the parental care expended for each offspring
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are characteristics of r-selected populations? (Check all that apply.)
A) early age of first reproduction
B) late age of first reproduction
C) small brood size
D) large brood size
E) little or no parental care
F) extensive parental care
G) short generation time
H) long generation time
I) type I survivorship curves
J) type III survivorship curves
L) C) and G)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are earning your Ph.D. in marine biology, studying the microbial ocean community. This year, you are shocked to discover that one of your study sites has become contaminated due to an industrial waste water pipe. This dumping is drastically raising the temperature and lowering the salinity of the water. What do you expect to find in your survey of the population, and what might you find in a survey years from now?
A) Most species will be wiped out this year, and in subsequent years even fewer will remain.
B) The individuals will turn on genes to adapt to these changes, and the populations will end up largely the same this year and following years.
C) Many species will have decreased or disappeared from this site, but later some species may increase in population if they acquire adaptive mutations. Also you may see some new species expand into the site.
D) Most species will be wiped out this year, and it will take millions of years for new species to evolve -- until then the site will be devoid of life.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population of squirrels is in a phase of exponential growth. What events would act to slow this growth? (Check all that apply.)
A) a forest fire that destroys habitat
B) logging of nut trees
C) growth of the hawk population
D) heavy rainfall, resulting in larger seed and nut harvest
E) increased population that is outstripping food supply
F) less competition from a diminished population of ground squirrels
H) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rancher is suspected of shooting wolves near Yellowstone National Park, and you have been enlisted to go have a chat with him. The rancher doesn't see any benefit to having the wolves there. What do you say?
A) "If there are no predators like wolves, just one pair of jackrabbits can quickly create a population with explosive, logistic growth. Wolves help reduce the fecundity rate, keeping the population at a reasonable level."
B) "If there are no predators like wolves, just one pair of jackrabbits can quickly create a population with explosive, exponential growth. Wolves help reduce the carrying capacity, keeping the population at a reasonable level."
C) "If there are no predators like wolves, just one pair of jackrabbits can quickly create a metapopulation. Wolves help reduce the biotic potential, keeping the population at a reasonable level."
D) "If there are no predators like wolves, just one pair of jackrabbits can quickly create a population with explosive, density-dependent growth. Wolves help reduce the age structure, keeping the population at a reasonable level."
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 16 of 16
Related Exams