A) The difference in the density of stomata on the two leaf surfaces is not likely due to an adaptation related to gas exchange regulation.
B) The difference in the density of stomata on the two leaf surfaces is likely due to specific mechanisms that sunflowers use to disperse their seeds.
C) The difference in the density of stomata on the two leaf surfaces is likely due to mycorrhizal associations with other plants.
D) The difference in the density of stomata on the two leaf surfaces is likely due to different pollination needs for each surface.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In plants, the vascular tissue that consists of living cells that distribute sugars throughout the plant is called
A) xylem.
B) phloem.
C) conducting tissue.
D) meristem.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which part of this figure represents the anther? 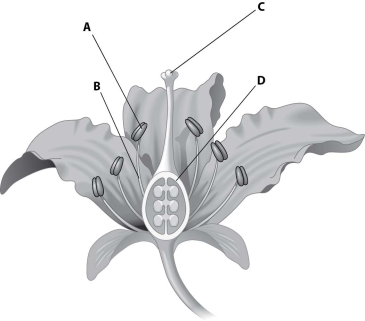
A) structure A
B) structure B
C) structure C
D) structure D
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs in the sexual reproduction phase of the fungus life cycle?
A) Hyphae of two different mating types fuse.
B) Diploid nuclei form, undergo meiosis, and produce haploid spores.
C) Heterokaryotic cells separate to re-create the original haploid hyphae.
D) Spores germinate and form a haploid mycelium.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many flower traits are specifically attractive to a certain type of pollinator. For example, the scent of rotting flesh is attractive to certain flies and beetles but not to most other pollinators. What adaptive purpose is served by this kind of "niche marketing" of flowers to specific pollinators?
A) This adaptation works to reduce pollinator traffic at a flower. Therefore, flowers do not have to produce as much nectar to feed big crowds of pollinators.
B) This adaptation reduces pollinator traffic so that flowers have a chance to develop their pollen fully before it is spread.
C) This targeting is done because the wrong kind of pollinator might eat all the pollen instead of delivering it to another flower.
D) This adaptation helps to assure that pollen will be delivered to another flower of the same species. If less specialized pollinators are used, the odds are greater that pollen will wind up on the stigma of a different species.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What kind of entity is a lichen?
A) an association between a fungus and a brown alga
B) an association between a multicellular protist related to the brown algae and a bacterium
C) an association between a fungus and cyanobacteria or green algae
D) an association between a bryophyte and a fungus
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The majority of plant species today are
A) angiosperms.
B) bryophytes.
C) gymnosperms.
D) seedless vascular plants.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you take two young cuttings of a house plant. You cut the roots off of one cutting and then place both cuttings in a jar of red dye. After 20 minutes, the roots, stem, and leaves of the cutting with roots have turned pink. The cutting without roots has not changed color at all. Why has the cutting without roots remained a normal, green color?
A) Cutting the roots has damaged the xylem, so the plant can no longer take up water.
B) Cutting the roots has damaged the phloem, so the plant can no longer take up water.
C) Cutting the roots has damaged the apical meristem, so the plant can no longer take up water.
D) Cutting the roots has damaged the sporangia, so the plant can no longer take up water.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gangrene, hallucinations, temporary insanity, and even death can result when humans consume grain infested with
A) corn smut.
B) chytrids.
C) coccidioidomycosis.
D) ergots.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a moss, most of the plants that we see are ________, and in a fern, the most dominant stage is the ________.
A) gametophytes; gametophyte
B) gametophytes; sporophyte
C) sporophytes; gametophyte
D) sporophytes; sporophyte
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In plants, the vascular tissue made of dead cells that transport water and minerals from the roots is called
A) xylem.
B) phloem.
C) conducting tissue.
D) meristem.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some of the unique adaptations of angiosperms include their beneficial relationships with ________ and their relatively ________.
A) animals; well-developed vascular system
B) animals; rapid fertilization and seed production
C) animals; large sporophyte
D) fungi; well-developed vascular system
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow. Scientists believe that a shift from pollination by insects to pollination by birds occurred several times over the course of angiosperm evolution. Two researchers designed an experiment to investigate how these shifts might evolve using two species of monkey flower (Mimulus spp.) . M. lewisii has violet-pink flowers and is pollinated by bumblebees. M. cardinalis has orange-red flowers and is pollinated by hummingbirds. The researchers switched flower-color genes between the two species. As a result of the gene transfer, they produced a variation of M. cardinalis with dark pink flowers (instead of the original orange-red) and a variation of M. lewisiis with orange flowers (instead of the original violet-pink) . Plants of both genetically altered varieties were placed in their original habitats and observed. The genetically altered variety of M. cardinalis was visited by bumblebees 74 times more often than plants with the original color flowers. The genetically altered variety of M. lewisii was visited by hummingbirds 68 times more often than plants with the original color flowers. -Based on the results of this study, you can conclude that
A) petal color won't contribute to speciation, since pollinators will select familiar plant species regardless of petal color.
B) gene mutations that affect petal color will also affect nectar production.
C) gene mutations affecting petal color can contribute to speciation through a shift in pollinator species.
D) flower color does not appear to be an important factor in the speciation of flowering angiosperms.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following organisms has a dominant sporophyte generation and a free-living gametophyte generation?
A) moss
B) fern
C) mushroom
D) conifer
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A comet orchid has creamy white-colored flowers and a characteristic "tail" that contains the flower's nectar. This orchid does not emit a scent during daylight hours but is aromatic at night. The comet orchid is most likely pollinated by
A) windy nighttime conditions.
B) pollen traveling on animal fur.
C) a nocturnal pollinator.
D) moisture from cool evenings.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures is an essential part of most fungal reproductive systems?
A) gametangia
B) cellulose
C) seeds
D) spores
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characteristics tends to limit bryophytes and seedless vascular plants to habitats that are relatively moist?
A) absence of cuticle
B) presence of flagellated sperm
C) presence of free-living, independent zygotes and early embryos
D) presence of lignified vascular tissues
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ represents the sporophyte generation of a conifer, and the ________ produces gametophytes.
A) cone; tree
B) tree; cone
C) tree; pollen
D) seed; tree
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Gymnosperms have seeds that are not enclosed in a protective casing, while angiosperms have flowers that produce seeds with a protective casing.
B) Gymnosperms have flowers that produce seeds with a protective casing, while angiosperms have seeds that are not enclosed in a protective casing.
C) Gymnosperms lack true roots and leaves, while angiosperms lack lignin cell walls.
D) Gymnosperms lack seeds, while angiosperms have flowers that produce seeds with a protective casing.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fungi contact and absorb food through the ________, a branching network of ________.
A) mycelium; hyphae
B) hyphae; mycelia
C) mycorrhiza; mushrooms
D) mushroom; hyphae
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 79
Related Exams