A) U.S.dollar, the euro, the Indian rupee, and the Chinese Yuan.
B) U.S.dollar, the euro, the pound sterling, and the Swiss franc.
C) U.S.dollar, the euro, the Swiss franc, and the yen.
D) U.S.dollar, the euro, the pound sterling, and the yen.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A "Eurobond" issue is
A) one denominated in a particular currency but sold to investors in national capital markets other than the country that issued the denominating currency.
B) usually a bearer bond.
C) for example a Dutch borrower issuing dollar-denominated bonds to investors in the U.K., Switzerland, and the Netherlands.
D) all of the above
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bond market index
A) is a reference rate, like LIBOR, that adjustable rate bonds use to set the coupon.
B) is analogous to a stock market index, but with bond price data instead of stock price data.
C) represents a price-weighted average of all bonds that exist.
D) none of the above
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Investment grade" ratings are in the following categories:
A) Moody's: AAA to BBB - S&P's: Aaa to Baa
B) Moody's: Aaa to Baa - S&P's: AAA to BBB
C) Moody's: AAA to A - S&P's: Aaa to A
D) Moody's: Aaa to A - S&P's: AAA to A
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a bond with an equity warrant.The warrant entitles the bondholder to buy 25 shares of the issuer at €50 per share for the lifetime of the bond.The bond is a 30-year zero coupon bond with a €1,000 par value that has a yield to maturity of i€ = 5 percent.The price of the bond is €500.What is the value of the warrant?
A) €231.38
B) €268.62
C) €500
D) none of the above
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Because __________ do not have to meet national security regulations,name recognition of the issuer is an extremely important factor in being able to source funds in the international capital market.
A) Eurobonds
B) Foreign bonds
C) Bearer bonds
D) Registered bonds
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Securities sold in the United States to public investors must be registered with the SEC,and a prospectus disclosing detailed financial information about the issuer must be provided and made available to prospective investors.This encourages foreign borrowers wishing to raise U.S.dollars to use
A) the Eurobond market.
B) their domestic market.
C) bearer bonds.
D) none of the above
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Find the present value of a 2-year Treasury bond that pays a semi-annual coupon,has a coupon rate of 6%,a yield to maturity of 5%,a par value of $1,000 when the yield to maturity is 5%.
A) $1,018.81
B) $1,231.15
C) $699.07
D) none of the above
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
U.S.corporations
A) are allowed to issue bearer bonds to non-U.S.citizens.
B) are not allowed to issue bearer bonds.
C) are allowed to issue treasury bonds but not T-bills.
D) none of the above
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Publicly traded Yankee bonds must
A) meet the same regulations as U.S.domestic bonds.
B) meet the same regulations as Eurobonds if sold to Europeans.
C) meet the same regulations as Samurai bonds if sold to Japanese.
D) none of the above
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Samurai" bonds are
A) dollar-denominated foreign bonds originally sold to U.S.investors.
B) yen-denominated foreign bonds originally sold in Japan.
C) pound sterling-denominated foreign bonds originally sold in the U.K.
D) none of the above
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Find the value of a three-year dual currency bond with annual coupons (paid in U.S.dollars at a 5 percent coupon rate) that pays £500 per $1,000 par value at maturity.The cash flows of the bond are: 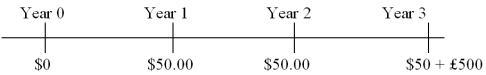 The dollar-based yield to maturity is i$ = 3%; the spot exchange rate is $1.80 = £1.00; expected inflation over the next three years is $ = 2% in the U.S.and £ = 3% in the U.K.
The dollar-based yield to maturity is i$ = 3%; the spot exchange rate is $1.80 = £1.00; expected inflation over the next three years is $ = 2% in the U.S.and £ = 3% in the U.K.
A) $927.62
B) $941.30
C) $965.06
D) 987.06
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In terms of the types of instruments offered,
A) the Yankee bond market has been more innovative than the international bond market.
B) the international bond market has been much more innovative than the U.S.market.
C) the most innovations have come from Milan, just like any other fashion.
D) none of the above
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1-year,4 percent pound denominated bond sells at par.A comparable risk 1-year,5.5 percent pound/dollar dual-currency bond pays $2,000 at maturity per £1,000 of face value.It sells for £900.What is the implied direct $/£ exchange rate at maturity?
A) £0.4405/$1.00
B) $1.2048/£1.00
C) $2.2701/£1.00
D) $2.0000/£1.00
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A five-year floating-rate note has coupons referenced to six-month dollar LIBOR,and pays coupon interest semiannually.Assume that the current six-month LIBOR is 6 percent.If the risk premium above LIBOR that the issuer must pay is 1/8 percent,the next period's coupon rate on a $1,000 face value FRN will be:
A) $29.375
B) $30.000
C) $30.625
D) $61.250
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Floating-rate notes (FRN)
A) experience very volatile price changes between reset dates.
B) are typically medium-term bonds with coupon payments indexed to some reference rate (e.g.LIBOR) .
C) appeal to investors with strong need to preserve the principal value of the investment should they need to liquidate prior to the maturity of the bonds.
D) both b and c
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The credit rating of an international borrower
A) depends on the volatility of the exchange rate.
B) depends on the volatility, but not absolute level, of the exchange rate.
C) is usually never higher than the rating assigned to the sovereign government of the country in which it resides.
D) is unrelated to the rating assigned to the sovereign government of the country in which it resides.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
U.S.citizens must pay tax on the imputed interest represented by the fact that zero coupon bonds price gets a bit closer to par value as each year goes by.If you have a 25-year zero coupon bond with $1,000 par value,how much imputed interest will you record in the coming year if interest rates stay the same at ten percent?
A) $92.30
B) $9.23
C) $0
D) none of the above
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assuming that the bond sells at par,the implicit $/£ exchange rate at maturity of a British pound-U.S.dollar dual currency bonds that pay £581.40 at maturity per $1,000 of par value is:
A) $1.95/£1.00
B) $1.72/£1.00
C) $1.58/£1.00
D) $0.5814/£1.00
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a British pound-U.S.dollar dual currency bonds that pay £581.40 at maturity per $1,000 of par value.If at maturity,the exchange rate is $1.90 = £1.00,
A) you should insist on getting paid in dollars.
B) investors holding this bond are better off for the exchange rate.
C) the issuer of the bond is worse off for the exchange rate.
D) both b and c
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 99
Related Exams