A) amnion.
B) yolk sac.
C) inner cell mass.
D) chorion.
E) blastocoel.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amnion is one of the extraembryonic membranes,and its function is to
A) prevent desiccation of the embryo.
B) allow fluid to enter the placenta.
C) form the plasma portion of the blood.
D) give the embryo nourishment.
E) permit implantation to occur.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reduction division occurs during
A) mitosis.
B) meiosis.
C) both mitosis and meiosis.
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From which primary germ layer is the thyroid gland derived?
A) Ectoderm
B) Mesoderm
C) Endoderm
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Trisomy refers to
A) the development of three primary germ layers.
B) three layers of cells.
C) the formation of triplets.
D) there being three copies of a given chromosome instead of two.
E) the formation of the three extra-embryonic membranes.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Differentiation refers to the
A) moment of conception (when sperm and egg unite) .
B) time when the blastocyst implants in the uterine wall.
C) formation and organization of the diverse cell types in the body.
D) formation of the various organ systems in the body.
E) separation of the placenta from the fetus at birth.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From which primary germ layer is the nervous system derived?
A) Ectoderm
B) Mesoderm
C) Endoderm
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During this critical period the subcutaneous fat is deposited and testes descend into the scrotum.
A) Weeks 1-8
B) Weeks 9-12
C) Weeks 13-16
D) Weeks 17-20
E) Weeks 21-38
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The secondary oocyte enters into an arrested state during its development.In what stage of development does this occur?
A) During metaphase I
B) During telophase I
C) During prophase II
D) During metaphase II
E) During telophase II
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This figure shows a superior view of the developing embryo.What structure does number 1 indicate?
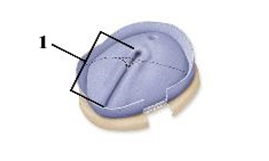
A) Yolk sac
B) Notochord
C) Primitive streak
D) Epiblast
E) Hypoblast
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens to the polar bodies that are produced during oogenesis?
A) They participate in the formation of the extra-embryonic membranes.
B) They provide yolk to nourish the early embryo.
C) They help to form the placenta.
D) They degenerate.
E) They are incorporated into the inner cell mass.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Formation of the neural tube
A) begins at the anterior (head) end and proceeds toward the posterior (tail) .
B) begins at the posterior and proceeds toward the anterior.
C) begins in the middle and proceeds toward the head and the tail.
D) is random in that it can begin and proceed at any location along the neural plate.
E) is caused by compaction of the neural plate.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major difference between oogenesis and spermatogenesis is that each cycle of oogenesis results in
A) four viable eggs,whereas a single cycle of spermatogenesis produces only one sperm.
B) three viable eggs,whereas a single cycle of spermatogenesis produces only one sperm.
C) only one viable egg,whereas a single cycle of spermatogenesis produces four spermatozoa.
D) three viable polar bodies,whereas a single cycle of spermatogenesis produces no polar bodies.
E) a tiny viable egg,whereas a single cycle of spermatogenesis produces four sperm,each much larger than the egg.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurulation is an example of
A) compaction.
B) blastulation.
C) gastrulation.
D) induction.
E) organogenesis.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would happen if more than one sperm penetrated a secondary oocyte,an event termed polyspermy?
A) Identical twins would result.
B) The sperm with the most advanced chromosomes would merge with the female nucleus.
C) The extra sperm would most likely fertilize one of the polar bodies.
D) The resulting zygote would not develop.
E) This never happens due to genetic controls.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A double-stranded chromosome consists of two genetically identical sister chromatids.What important biological event produced the sister chromatids?
A) Crossing over
B) Genetic mutation
C) Mitosis
D) DNA replication
E) Reduction division
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of embryogenesis includes
A) gastrulation.
B) fertilization.
C) gametogenesis.
D) formation of a zygote.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When does the embryonic period officially begin?
A) With the onset of cleavage
B) At the time of implantation
C) With the establishment of the three primary germ layers
D) When the umbilical cord becomes functional
E) At fertilization
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two standard measurements are used to determine fetal length.Which of these would be the longer of the two measurements on any normal fetus?
A) CHL
B) CRL
C) HTL
D) HRL
E) CFL
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At its formation,a morula consists of ______ cells.
A) 4
B) 8
C) 16
D) 32
E) 64
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 77
Related Exams